Office Ergonomics - Sit/Stand Desk
On this page
Why use a sit/stand desk?
Back to topA sit/stand desk is one that allows the user to alternate between sitting and standing by being able to lower or raise the work (desk) platform. In general, it is believed that by being able to alternate sitting and standing, users can vary their body position more often. Some disadvantages include the cost of the desk, and standing too long which may lead to foot, knee, hip, and back issues.
If you choose to use a sit/stand desk, remember that proper ergonomic set-up is very important. It is essential to make sure the desk meets the needs of the user when both standing and sitting.
How should a sit/stand desk be set up?
Back to topMaintain a neutral body position when both sitting and standing:
- Hands, wrists, and forearms are straight, in-line and roughly parallel to the floor.
- Head is level, forward facing, and balanced. Generally speaking, the head is in-line with the torso.
- Erect or upright spine.
- Shoulders are relaxed and upper arms hang normally at the side of the body.
- Elbows stay close to the body and are bent at about 90 degrees.
- No twisting of the upper torso.
- The in-line sight is between the horizontal and 30 degrees below the horizontal (i.e., when viewing the monitor, the monitor is at eye level or slightly below eye level).
For information about ergonomics for sitting positions, please see the OSH Answers documents on Working in a Sitting Position and Office Ergonomics.
When the desk is in the standing position, be sure that:
- The platform height is approximately at your standing elbow position (e.g., your arms are in the same position as they would be if you were sitting).
- The keyboard and mouse are aligned as you would when you are sitting.
- The height of the monitor should still be between horizontal and 35 degrees below.
- Wear supportive footwear.
- Consider the use of an anti-fatigue mat, where appropriate.
- Use a footrest when standing to help shift your weight as needed, or shift your weight from leg to leg occasionally.
- Make sure that any cables, electrical access, storage of materials, and general layout do not make adjusting the desk difficult.
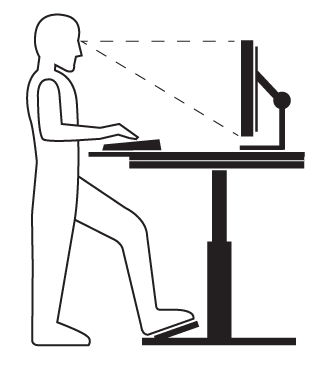
Figure 1 - Standing at desk
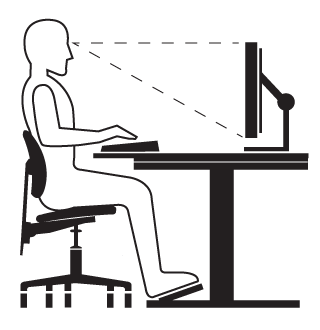
Figure 2 - Sitting at desk
How long should a person sit or stand?
Back to topRecommendations vary from sitting for 1 hour and standing for 5 minutes, to switching between sitting and standing for 20, 30, 45, or 60 minutes. Your health professional may also make recommendations. The key factor is to alternate your position as needed. Allow time for your body to adjust to your new routine. Early studies have indicated that some users tend to return to sitting for the majority of the time after the initial trial period of time. To achieve the benefits of being able to alternate body positions, be sure to continue to do so.
Remember, it is also important to still take breaks away from the computer to help alleviate eye strain and to vary the position of the head, upper body, arms, and hands.
- Fact sheet last revised: 2022-11-30

