Eye and Face Protectors
On this page
- When are eye and face protectors required?
- What types of equipment are available to protect the eyes and face?
- How do I recognize safety eye wear?
- What are the pros and cons of the different lenses?
- What should I know about the fit and care of eye wear?
- What should I know about lens colours?
- How do I select the proper eye and face protection?
- What types of eye and face protection can be used to help protect against respiratory infectious diseases?
- What types of eye and face protection can be used to protect against chemical hazards?
When are eye and face protectors required?
Back to top
In general, eye and face protection needs to be worn whenever there is a risk to a worker that could result in an injury or harmful exposure to a worker’s eyes or face. These hazards are associated with:
- Flying objects, particles, and dust (e.g., grinding, cutting, hammering, sawing)
- Splashes (including droplets and sprays) from chemicals and other liquids
- Radiation (e.g., welding) and lasers
- Abrasive and molten material
Check the legislation in your jurisdiction to determine the requirements for eye and face protection. Many jurisdictions in Canada require eye and face protection to meet CSA Standard Z94.3 Eye and Face Protectors.
Workplaces should conduct hazard assessments to identify the hazards that workers may be exposed to, and then select appropriate personal protective equipment when engineering controls or other more permanent methods of control are not possible. Consult with the personal protective equipment manufacturer about the uses and limitations of each type of eye and face protection.
If using personal protective equipment is part of the work, the workplace should develop and implement a personal protective equipment program. A good comprehensive strategy involves considering the hazards, conducting risk assessments, evaluating all possible control methods, integrating various approaches, and re-examining the controls frequently to make sure that the hazard continues to be controlled.
What types of equipment are available to protect the eyes and face?
Back to top
Below is a brief description of different types of eye and face protection (see tables further below for more detailed information),
Safety glasses or spectacles
- Protect eyes from impact hazards (e.g., flying objects and particles).
Goggles
- Direct ventilated goggles which protect against impact hazards
- Non-ventilated and indirect ventilated goggles which protect against impact hazards, chemical or liquid splashes, and fine dusts.
- Goggles specifically designed for protection against non-ionizing radiation and lasers are also available.
Face Shields
- Helps protect the eyes, nose, mouth, and face from impact hazards and chemical or liquid splashes (including saliva).
- Face shields are also available to protect against non-ionizing radiation, high heat and electric arcs.
- When used for protection from respiratory infectious diseases, face shields can offer benefits such as protection from respiratory particles produced from coughing or sneezing, and from splashed bodily fluids (e.g., blood and saliva).
Welding Helmets
- Protects eye and face from radiation, weld splatter, and impact hazards associated with certain activities (e.g., welding, torch cutting, brazing).
Hoods
- Protects eye and face from impact hazards, dust, splashes, and abrasive material. Hoods are also available to protect against non-ionizing radiation, high heat and electric arcs.
Respirator facepieces
- Full-face respirators provide a seal or partial seal (e.g., loose-fitting hood or helmet) around the perimeter of the face. Protects eye and face from chemical exposures, fine dusts and particles, liquid splashes, and impact hazards (lens in the respirator must meet the same impact protection standards as safety glasses and face shields).
- Respirator facepieces are also available to protect against non-ionizing radiation.
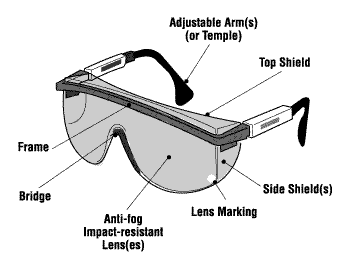
How do I recognize safety eye wear?
Back to topLenses: CSA-certified eye and face protectors must meet the criteria for impact resistance as outlined in the standard. Only devices made of approved materials are permitted.
Markings: The manufacturer or supplier certification mark must be present on all approved safety lenses, frames (front and temple), removable side shields, and other parts of the glasses, goggles, or helmets. Products that are tested and approved by CSA will bear the CSA certification mark.
Frames: Safety frames are stronger than street-wear frames and are often heat resistant. They are also designed to prevent lenses from being pushed into the eyes.
What are the pros and cons of the different lenses?
Back to top| Comparison of Lens Materials | |
|---|---|
| Material | Characteristics |
| Hi-Vex |
|
| Polycarbonate |
|
| Plastic (CR39) |
|
| Trivex |
|
| Glass |
|
From: CSA Standard Z94.3.1-16 Guideline for selection, use and care of eye and face protectors, 2016
What should I know about the fit and care of eye wear?
Back to topEye wear will protect the user if the protection device fully covers the eye and surrounding soft tissues. If eye protection is required, establish a complete eye safety protection program, including selection, fit testing, training, maintenance, and inspection.
Fit
- Ensure your safety eye wear fits properly. Eye wear should cover from the eyebrow to the cheekbone and across from the nose to the bony area on the outside of the face and eyes. Eye size, bridge size and temple length all vary. Eye wear should be individually assigned and fitted so that gaps between the edges of the device and the face are kept to a minimum.
- Eye wear should fit over the temples comfortably and over the ears. The frame should be as close to the face as possible and adequately supported by the bridge of the nose.
- Users should be able to see in all directions without any major obstructions in their field of view.
- Face shields should extend below the chin and above the eyes, and should wrap around the sides of the face
Care
Eye and face protection devices need maintenance.
- Clean your devices daily and as often as necessary. Follow the manufacturer's instructions.
- Avoid rough handling that can scratch lenses. Scratches impair vision and can weaken lenses.
- Store your devices in a clean, dry place where they cannot fall or be stepped on. Keep them in a case when they are not being worn.
- Replace scratched, pitted, broken, bent or ill-fitting devices immediately. Damaged devices interfere with vision and do not provide protection.
- Replace damaged parts only with identical parts from the original manufacturer to ensure the same safety rating.
- Do not change or modify the protective device.
What should I know about lens colours?
Back to topLenses can be clear, tinted, photochromic or polarized. Each type offers various levels of ultraviolet protection, including no protection (even when coloured). Do not be fooled by the colour of the lenses.
How do I select the proper eye and face protection?
Back to topIf you are at risk for eye or face injury at work, you should wear appropriate protection.
To select the proper protectors, follow the recommendations in the table below.
Note: This table cannot cover all possible hazards and combinations that may occur. Examine each situation carefully and select the appropriate protector or combination of protectors.
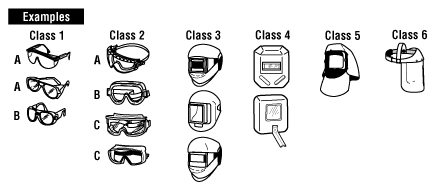
| Nature of hazard | Hazardous Activities involving but not limited to | Recommended protectors |
|---|---|---|
| Flying Objects | Chipping, scaling, stonework, drilling, grinding, buffing, polishing, hammer mills, crushing, heavy sawing, planing, wire and strip handling, hammering, unpacking, nailing, punch press, lathework | Class 1A - Spectacles Class 2A, 2B - Goggles Class 5A, 5B - Hoods Class 6A, 6D - Face shields |
| Flying particles, dust, wind, etc. | Woodworking, sanding, light metal working and machining, exposure to dust and wind, resistance welding (no radiation exposure), sand, cement, aggregate handling, painting, concrete work, plastering, material batching and mixing | Class 1A - Spectacles Class 2A, 2B - Goggles Class 5A, 5B - Hoods Class 6A, 6D - Face shields |
| Heat, sparks, and splash from molten materials | Babbiting, casting, pouring, molten metal, brazing, soldering, spot welding, stud welding, hot dipping operations | Class 1B - Spectacles Class 2C - Goggles Class 5C, 5D - Hoods Class 6B, 6C, 6D - Face Shields |
| Acid splash, chemical burns | Acid and alkali handling, degreasing, pickling and plating operations, glass breakage, chemical spray, liquid bitumen handling | Class 2B - Goggles Class 5B - Hoods Class 6A - Face Shields |
| Abrasive blasting materials | Sand blasting, shot blasting, shotcreting | Class 2B - Goggles Class 5B - Non-Rigid Hoods Class 6A - Face Shields |
| Glare, stray light (where slight reduction of visible radiation is required) | Reflection, bright sun and lights reflected welding flash, photographic copying | Class 1A - Spectacles Class 2A, 2B - Goggles Class 5A, 5B - Hoods Class 6A - Face Shields |
| Injurious optical radiation (where moderate reduction of optical radiation is required) | Torch cutting, welding, brazing, furnace work, metal pouring, spot welding, photographic copying | Class 1B - Spectacles Class 2C - Goggles Class 5C - Hoods Class 6B - Face Shields |
| Injurious optical radiation (where a large reduction of optical radiation is required) | Babbiting, casting, pouring, molten metal; brazing, soldering, spot welding, stud welding, hot-dipping operations | Class 3 - Helmet Class 4 - Handshield |
| Laser radiation | Laser cutting, laser surgery, laser etching | Class 2D - Goggles |
| Electric arc flash | Electrical installation, electrical maintenance, troubleshooting of electrical systems, disconnecting live electrical systems | Class 2E - Goggles Class 5E - Hoods Class 6D - Face shields |
From: CSA Standard Z94.3.1-16 Guideline for selection, use and care of eye and face protectors, 2016
What types of eye and face protection can be used to help protect against respiratory infectious diseases?
Back to topEye and face protection may also be required when there is a risk of exposure to infectious diseases that can be transmitted through respiratory droplets or other bodily fluids. Splashed body fluids may also increase the risk of other diseases such as hepatitis B and C, and HIV. Safety glasses, goggles, and face shields may be used as an additional layer of protection to help prevent infectious droplets from coming into contact with a worker’s eyes, nose or mouth. These devices are not substitutes for respiratory protection, and appropriate masks and respirators need to be worn when required.
What types of eye and face protection can be used to protect against chemical hazards?
Back to topSplashes, droplets and sprays:
- Goggles with indirect ventilation
- Face shield worn over goggles with indirect ventilation
- Loose-fitting respirator worn over safety glasses or goggles
- Full-face respirator
Irritating chemical mists:
- Goggles with no ventilation
- Face shield worn over goggles with no ventilation
- Loose-fitting respirator worn over safety glasses or goggles
- Full-face respirator
(based on guidance from ANSI Z87.1-2015 Personal Eye and Face Protection Devices)
Make sure the eye and face protection is appropriate for the hazards and is selected, used, and maintained in accordance with the applicable legislation and standards. If respirators are worn, the workplace must follow the requirements of their respiratory protection program.
- Fact sheet last revised: 2024-02-26

